What actually is Ransomware......!!
Ransomware is a type of malware that prevents or limits users from accessing their system, either by locking the system's screen or by locking the users' files unless a ransom is paid. More modern ransomware families, collectively categorized as crypto-ransomware, encrypt certain file types on infected systems and forces users to pay the ransom through certain online payment methods to get a decrypt key.
Ransom Prices and Payment
Ransom prices vary depending on the price or exchange rates of digital currencies. Thanks to the perceived anonymity offered by cryptocurrencies, ransomware operators commonly specify ransom payments in bitcoins. Recent ransomware variants have also listed alternative payment options such as iTunes and Amazon gift cards. It should be noted, however, that paying the ransom does not guarantee that users will get the decryption key or unlock tool required to regain access to the infected system or hostaged files.The Evolution:
Cases of ransomware infection were first seen in Russia between 2005 – 2006. Trend Micro published a report on a case in 2006 that involved a ransomware variant (detected as TROJ_CRYZIP.A) that zipped certain file types before overwriting the original files, leaving only the password-protected zip files in the user’s system. It also created a text file that acted as the ransom note informing users that the files can be retrieved in exchange for $300.In its earlier years, ransomware typically encrypted particular file types such as DOC, .XLS, .JPG, .ZIP, .PDF, and other commonly used file extensions.
In 2011, Trend Micro published a report on an SMS ransomware threat that asked users of infected systems to dial a premium SMS number. Detected as TROJ_RANSOM.QOWA, this variant repeatedly displayed a ransomware page to users until they paid the ransom by dialing a certain premium number.
Effect of ransomeware on world:
Ransomware Infection and Behavior
Users may encounter this threat through a variety of means. Ransomware can be downloaded onto systems when unwitting users visit malicious or compromised websites. It can also arrive as a payload either dropped or downloaded by other malware. Some ransomware are known to be delivered as attachments from spammed email, downloaded from malicious pages through malvertisements, or dropped by exploit kits onto vulnerable systems.Once executed in the system, ransomware can either lock the computer screen, or, in the case of crypto-ransomware, encrypt predetermined files. In the first scenario, a full-screen image or notification is displayed on the infected system's screen, which prevents victims from using their system. This also shows the instructions on how users can pay for the ransom. The second type of ransomware prevents access to files to potentially critical or valuable files like documents and spreadsheets.
Ransomware is considered "scareware" as it forces users to pay a fee (or ransom) by scaring or intimidating them. In this sense, it is similar to FAKEAV malware, but instead of capturing the infected system or encrypting files, FAKEAV shows fake antimalware scanning results to coax users into purchasing bogus antimalware software.
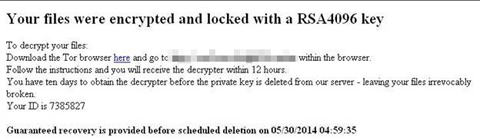
Once all files on the infected system are encrypted, it displays the following image:
Protect yourself from Becoming an Ransomeware victim
Ransomware Prevention:
- Avoid opening unverified emails or clicking links embedded in them.
- Back up important files using the 3-2-1 rule create 3 backup copies on 2 different media with 1 backup in a separate location.
- Regularly update software, programs, and applications to protect against the latest vulnerabilities.
RANSOMWARE
 Reviewed by Unknown
on
22:26
Rating:
Reviewed by Unknown
on
22:26
Rating:
 Reviewed by Unknown
on
22:26
Rating:
Reviewed by Unknown
on
22:26
Rating:





No comments: